Module 1: Effective Communication
OBJECTIVES:
- To understand different methods of communication
- To develop an understanding of how information is interpreted
- To explore ways of improving your own communication skills
Impact of messages:
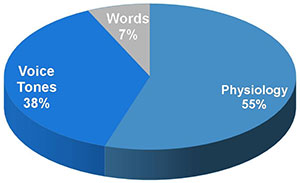
- 7% verbal
- 38% vocal (tone, pace and pitch)
- 55% Facial expression
Perception:

A learner’s response to your message is based on what they perceive you said. Due to prior learning, you are likely to see or hear what you expect to see or hear.
Read through this list of colors, instead of reading the word; say the color of each word (source)
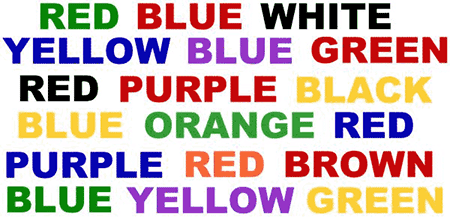
If you found this difficult, then you have demonstrated the effect of prior learning on your perception.
In the same way it is sometimes hard to really listen to the learner’s explanation of their performance because it differs from our established expectations. There is never just one way of seeing things…
What do you see below? (source)

In black you can read the word GOOD; but the word EVIL also appears in white letters inside each black letter.
ACTIVITY: Watch these short video clips below from “YOUTUBE” and reflect upon your learning.
YOUTUBE CLIP: Effective communication by Integration Training
Duration: 7.21 minutes
A short video by Mark Walsh giving 10 tips for effective communication.
YOUTUBE CLIP: Verbal and non-verbal communication
Duration: 4.38 minutes
A short video describing verbal and non-verbal communication with some cultural sensitivities.
REFLECTIVE EXERCISE: Observe some conversations at your workplace. What body language did you observe and was it consistent with the verbal content? Reflect upon your observations.
Communicating effectively
Effective communication skills, especially listening and questioning skills, are essential to effective facilitation of learning. Facilitating learning requires communication across a spectrum of situations and settings and in a variety of ways.
Tips to optimise effective communications:
- Ensure that the content of what is said matches the way it’s said and is reinforced by appropriate body language
- Be clear about the meaning that is being conveyed
- Minimise the possibility of distractions or interruptions.
Active Listening
The aim of active listening is to listen closely to the details that are being conveyed in order to ensure that not just the content is understood but also the intended message. The skill of active listening is important in the supervisory and learning relationships where feedback reflective practice and facilitation of clinical reasoning are required.
Qualities of an active listener:
- Is non-judgemental
- Has open body language
- Asks questions to facilitate learning
- Seeks clarification to enhance understanding
- Is genuinely interested
- Summarises frequently to endure understanding
- Is aware of tone and pays attention to nonverbal forms of communication in self and learner
- Seeks and gives feedback whenever possible
- Remains calm, in control and relaxed
- Allows time to articulate thoughts
- Paraphrases before disagreeing to demonstrate active listening and understanding
- Avoids making vague, unclear and ambiguous comments (HETI, May 2012).
